Which Drinks are Produced by Hot Filling Machine?
Views: 1003
Author: Site Editor
Publish Time: 2019-05-23
Origin: Site
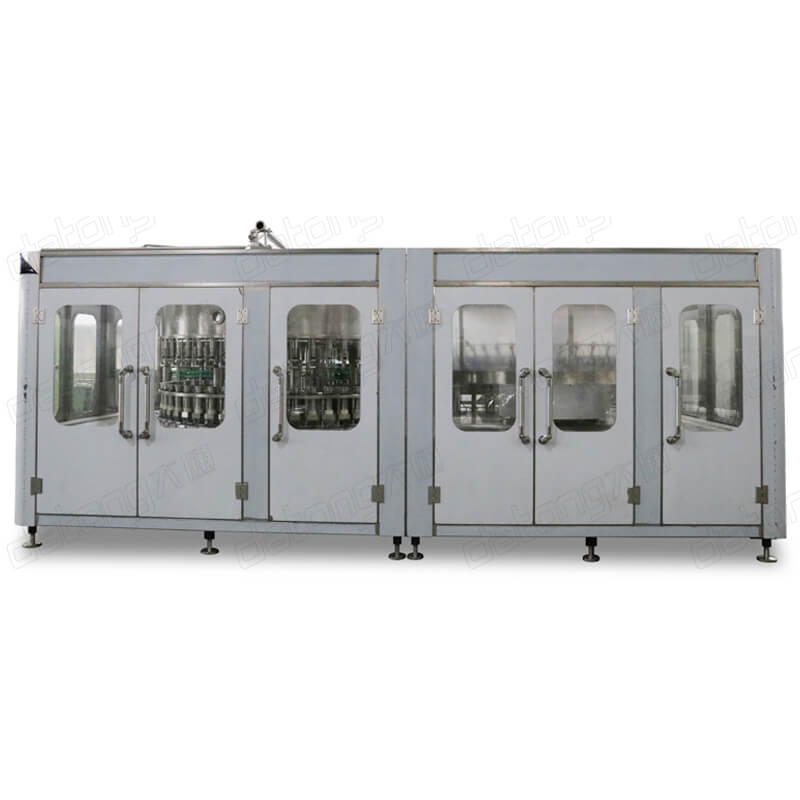
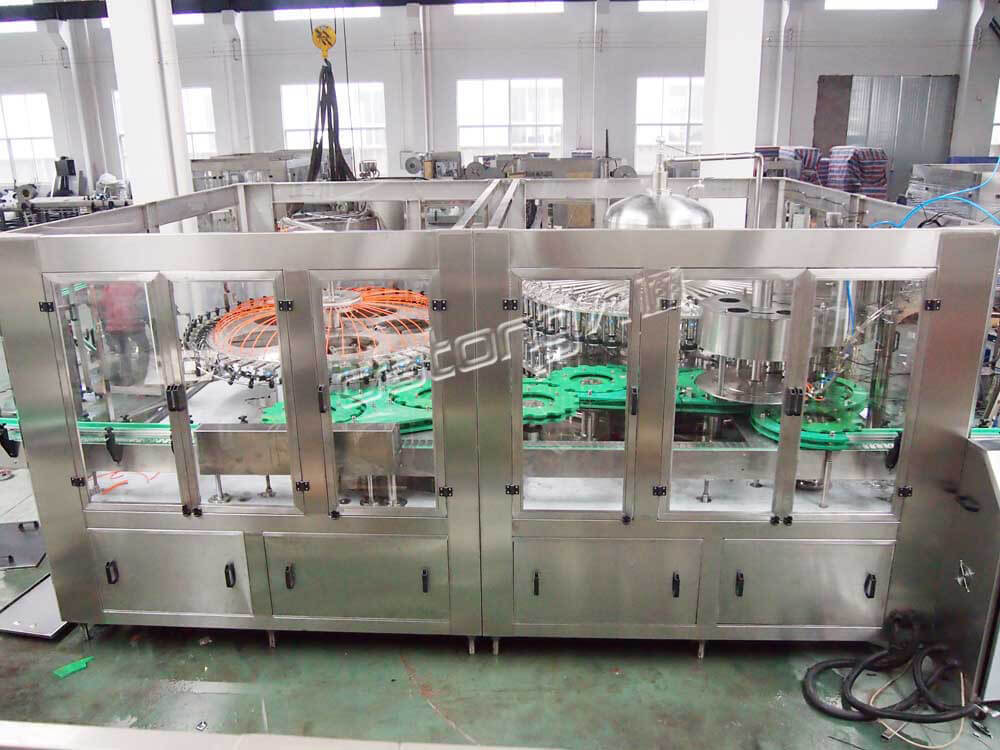
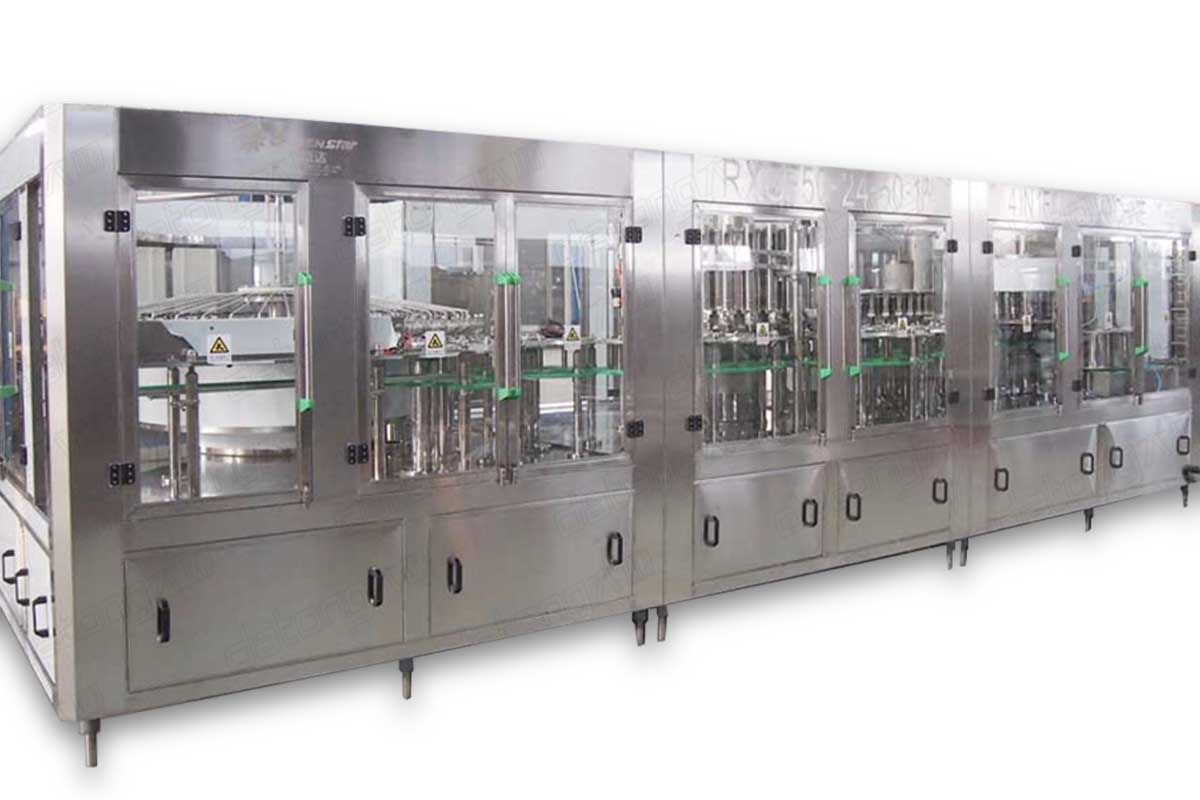
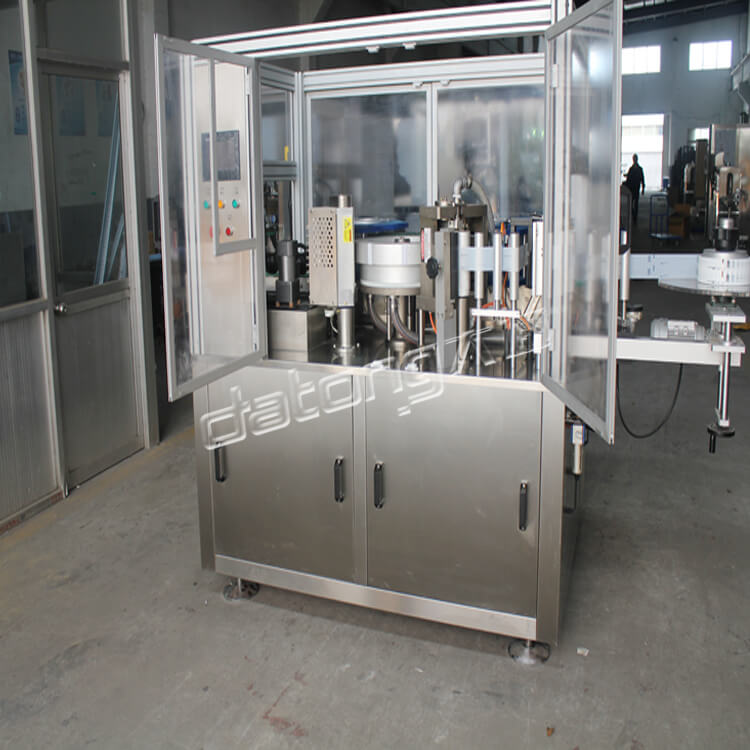
In the beverage industries, there are methods adopted in the production and packaging of beverages. One of them is the hot filling process. The hot filling is carried out using a special machine known as the hot filling machine. This machine is used in the production and packaging of a wide range of drinks. They include the following:
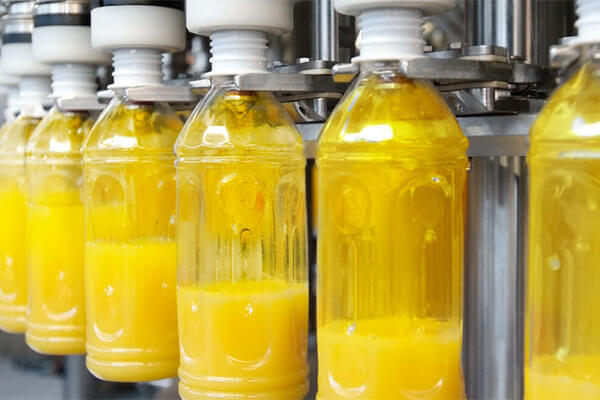

Juice: Juice is a special drink that basically consist of concentrates, extracts from fruits and water. During their packaging, special juice machines are utilized. One of such include the hot juice filling machine. The ‘hot’ implies that the liquid is introduced into their packaging containers in high temperatures. The idea here is to ensure a high level of purity of the product. The heat helps to eliminate spoilage microorganisms, maintain the nutritional properties and to extend the shelf life of the juice.
Tea: As known to most people, tea is better served when hot. Hence, the hot tea filling machine comprises of a heating unit which increases the temperature of the mixture before it is dispensed into the collecting bottle or container.
Now, let’s consider the hot filling machine process thus;
Step by step: how the hot filling or hot filling process is carried out
With the most recent developments it is possible that hot filling process can be carried out to pack liquid products in PET bottles. However, specific techniques needs to be used in this process to avoid deformations during and after filling since this thermoplastic polymer has a transition temperature which is approximately 70 ° C. The advances of the process have opened the possibility that the bottling can be done at temperatures of up to 85 degrees Celsius, which guarantees high hygiene conditions and preservation of the products.
The heat resistant preforms are now a common type of plastic container in many applications of hot - fill beverages. They are specifically made to withstand hot fill temperatures without losing the main characteristics of PET: lightweight and recyclable.
But how is the hot filling process carried out? Here we explain it in four steps.
Step 1: The beverage is pasteurized for at least 15-30 seconds the hot fill temperatures ranging between 190 to 203 in a heat exchanger. This process usually kills all the microorganisms in the liquid.
Step 2: The liquid is cooled to around 180 to 185 F (82-85 C) and the container is filled at the filling station. Nitrogen is introduced in some cases into the headspace (the empty space between the rim and the liquid) to remove oxygen in order to avoid oxidation. The closure of the container is applied immediately afterwards.
Step 3: The closed container is then put in a water bath to make sure that it cools quickly. This process helps to preserve the nutritional properties and flavor of the product. The cooling process also creates a vacuum inside the container, preventing microbial growth.
Step 4: The cold bottle is dried and the label is placed.